{{item.title}}
{{item.text}}

{{item.text}}
New technologies are changing the face of manufacturing—from 3D printing, robotics, the industrial Internet of Things, to autonomous vehicles.
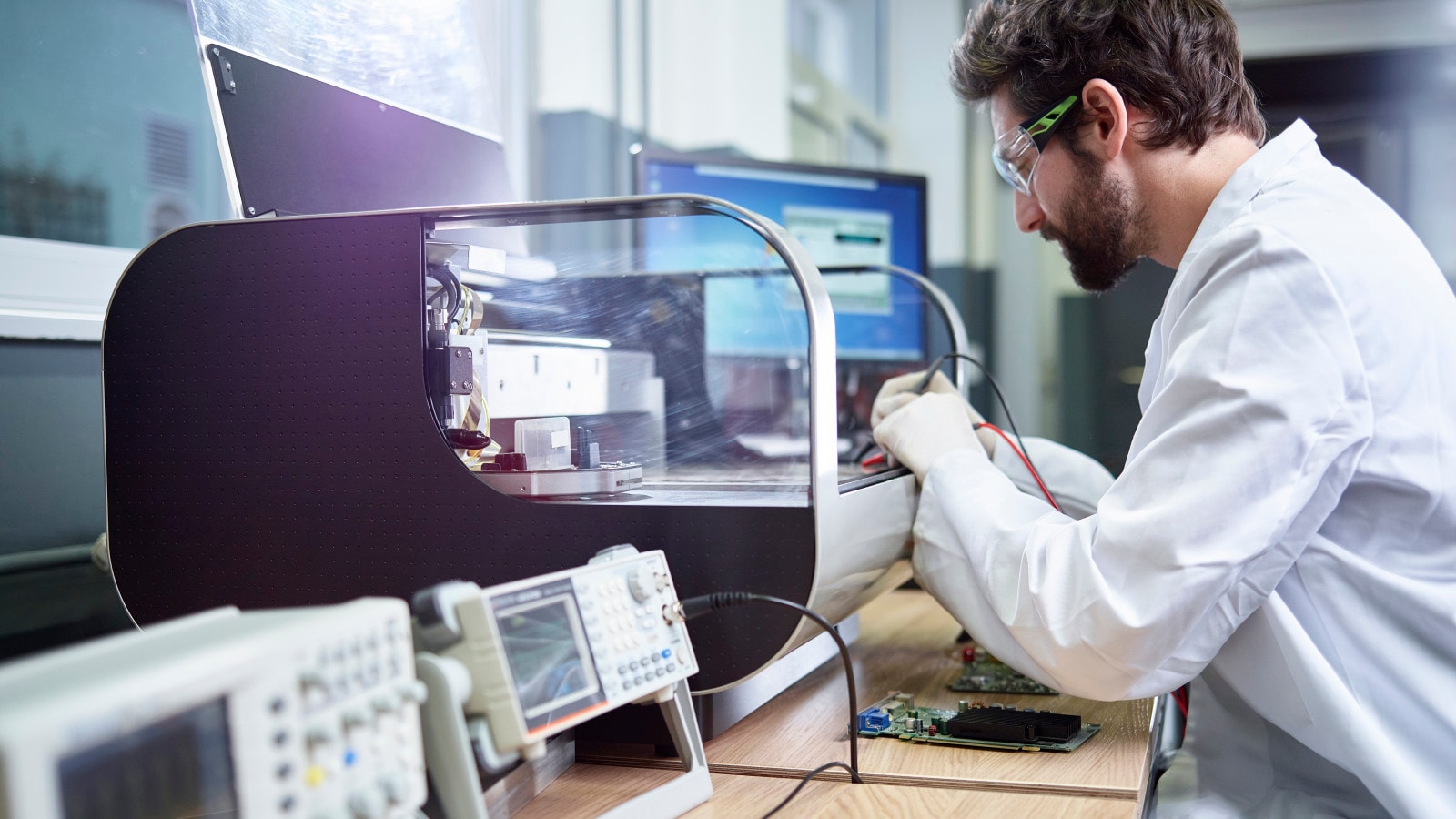

Factories are becoming increasingly connected, as machines talk to one another and to humans. Automation and autonomy reach new milestones, too, as robots become more independent, mobile and take on more human attributes.
But something else is happening. As manufacturing embraces the digital age, they are becoming as much the purveyors of things as they are producers and sellers of data and information. Manufacturers are now crossing a threshold as they seek new ways to commercialize not only their traditional products, but also new digital and IoT-enabled services stacked upon those products.
This is an exciting transformation, and one that will likely unfold in surprising ways. PwC will continue to tell this story of what’s next in manufacturing.
The IoT and digitalization of data are at the heart of today’s smart factory, enabling real-time connectedness—not only within the factory (robots teaching one another) but also outside its walls (products talking to their manufacturers). The rapid and wide deployment of data-gathering devices—and the analysis of that data—are transforming manufacturers from makers of things to makers (and sellers) of information.
How blockchain can transform defence assets and give armed forces an advantage on the battlefield
3D printing, robotics, sensors, virtual and augmented reality—collectively, disruptive technology—are changing the core of industrial manufacturing. Organizations that let their business strategy guide their 4IR investments—rather than the other way around—are better positioning themselves for success.
Today’s smart factories need workers that are technologically agile—from mentoring robots to making a 3D-printed part. As manufacturers adopt new technologies, they’re also filling a talent gap—recruiting from other industries, partnering with schools, upskilling workers and piloting apprenticeships.
Most advanced manufacturing technologies potentially can be vulnerable to cyber-attack. As manufacturers adopt new internet-based technologies, they will need to be especially vigilant to build safeguards that are as robust and innovative as their connected operations and products.
Autonomous forklifts, self-driving trucks and swarms of mobile robots... the movement of materials and product inside and outside factories and warehouses is changing in almost unimaginable ways. Manufacturers are already seeing how industrial mobility can cut costs, improve efficiencies and improve worker safety.
How autonomous vehicles can change manufacturing
Autonomous vehicles won’t just change our roads, they’ll change our factories, too








© 2017 - 2026 PwC. All rights reserved. PwC refers to the PwC network and/or one or more of its member firms, each of which is a separate legal entity. Please see www.pwc.com/structure for further details.