
Which regions will gain the most from AI?
Changing the game
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is going to be a big game changer in the global economy, and much of the value potential is up for grabs. We estimate that AI could contribute up to $15.7 trillion to the global economy in 20301, more than the current output of China and India combined. Of this, $6.6 trillion is likely to come from increased productivity and $9.1 trillion is likely to come from benefits to consumers.
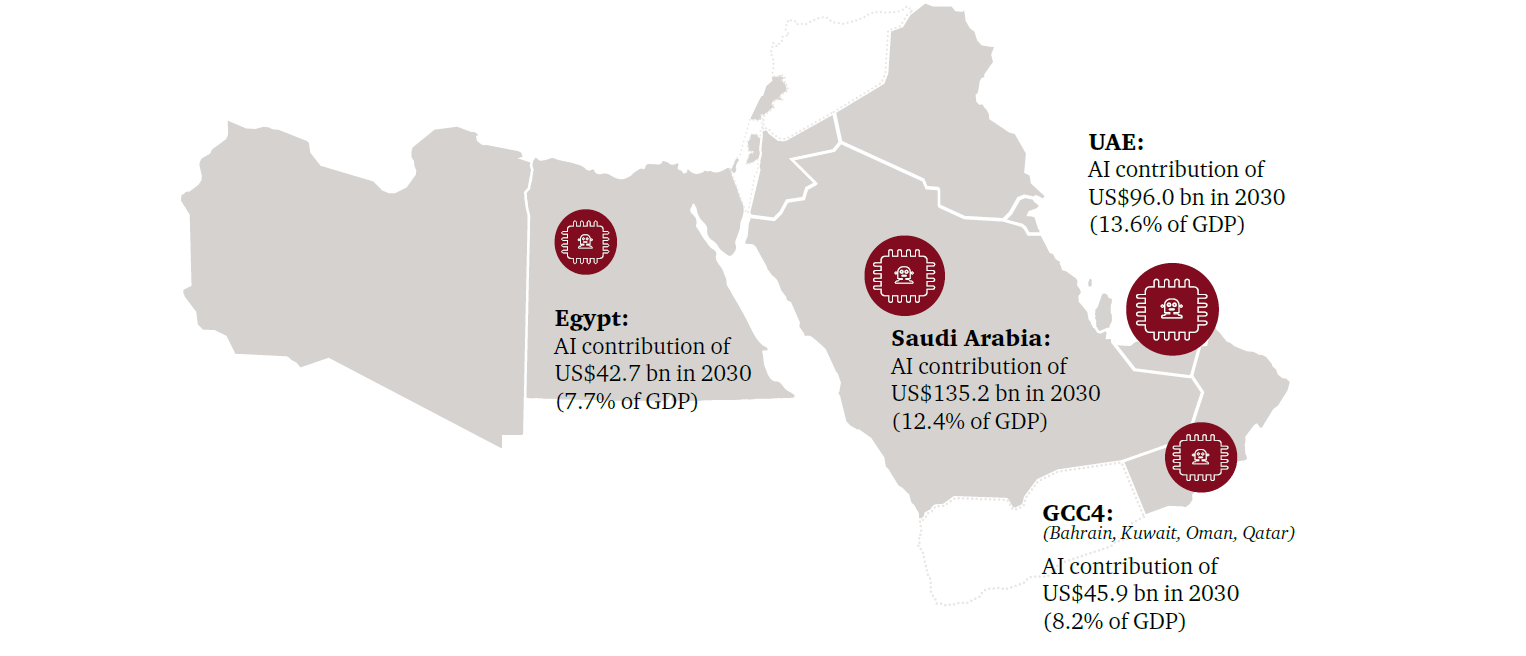
The US$320 billion impact of AI for the Middle East2
In the wake of the fourth industrial revolution, governments and businesses across the Middle East are beginning to realise the shift globally towards AI and advanced technologies. They are faced with a choice between being a part of the technological disruption, or being left behind. When we look at the economic impact for the region, being left behind is not an option. We estimate that the Middle East is expected to accrue 2% of the total global benefits of AI in 2030. This is equivalent to US$320 billion.
In absolute terms, the largest gains are expected to accrue to Saudi Arabia where AI is expected to contribute over US$135.2 billion in 2030 to the economy, equivalent to 12.4% of GDP. In relative terms the UAE is expected to see the largest impact of close to 14% of 2030 GDP.
The impact could be even larger if governments continue to push the boundaries of innovation and implementation of AI across businesses and sectors.
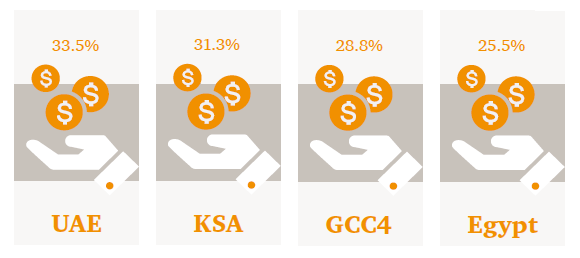
The annual growth in the contribution of AI is expected to range between 20-34% per year across the region, with the fastest growth in the UAE followed by Saudi Arabia.
The magnitude of the impact expected in these two economies is unsurprising given their relative investment in AI technology compared to the rest of the Middle Eastern region - both countries place within the top 50 countries in the world on the Global Innovation Index 20173 in terms of their ability to innovate and the outputs of their innovation.
Endless opportunities await
AI has the potential to fundamentally disrupt markets in the Middle East through the creation of innovative new services and entirely new business models. We’ve already seen the impact of the first wave of digitisation. With the eruption of AI, some of the market leaders in ten, even five years’ time may be companies you’ve never heard of.
Tomorrow’s market leaders are likely to be exploring the possibilities and setting their strategies today.
In its current scenario, the region is able to take their cut of the AI phenomenon and inject US$320 billion into the region. If governments and businesses nurture and mature AI to its fullest extent, there is so much more ‘up for grabs’ and endless opportunities await.
The average annual growth in the contribution of AI by region between 2018-2030
How can the region play to win?
The world is moving towards AI and in these early stages of development, there is an opportunity for the region to become a key player in the global agenda. Our ‘US$320 billion scenario’ takes into account what the region is doing now. However, there are greater, untapped opportunities that could increase the impact of AI on the region’s economy.
The current state of play
Parts of the region have already embraced AI and the new digital age. Analysis conducted by the International Data Corporation (IDC)4 estimates that spending on cognitive and artificial intelligence (AI) systems in the Middle East and Africa (MEA) region will grow from $37.5 million in 2017 to over $100 million by 2021, representing a growth rate of 32% a year.
Beyond 2030, the scope of AI impacts on both the economy and society will almost certainly increase, so it is important for the Middle East to be strategically placed in order to provide a springboard for the future.
The UAE, Saudi Arabia and Qatar, in particular, have demonstrated strong commitment towards the development and implementation of AI technologies. Businesses in these parts of the region have been investing heavily in new technology, supported by governments as early consumers of the technology. Outside the gulf economies, however, adoption has been slower. The differences in adoption levels are driven by differences in, for example, infrastructure and access to skilled labour, key enabling factors for AI development.
It’s important also to note that whilst the volatility in oil prices is taking its toll on the economic prospects of the region, it is creating the need for governments to seek alternative sources for revenue and growth. The development of non-oil sectors through investment in AI technologies could strategically position the region for the years to come.
United Arab Emirates
In the UAE, AI is at the forefront of the government’s strategic plans. In October 2017, the government launched its strategy for AI, demonstrating its commitment towards the technological enhancement of the nation. Alongside this strategy, HH Sheikh Mohammed Bin Rashid Al Maktoum, Vice President and Prime Minister of the UAE and Ruler of Dubai, appointed HE Omar Bin Sultan Al Olama as the first Minister of State for AI.
Within the UAE, Dubai is leading the way for AI. The Emirate’s strategies include, amongst others:
- A Smart Dubai strategy which aims to transform the city through innovation and digital transformation5, launching an
AI smart lab in 2017 focused on training public and private sector employees in implementing AI in their fields6 - A Dubai 3D Printing Strategy, targeted at the construction, medical products and consumer products sectors with a goal of having 25% of buildings in Dubai constructed using 3D printing technology by 20307
- A Dubai Autonomous Transportation Strategy, which aims to cut transportation costs by 44%, carbon emissions by 12% and accidents by 12% by transforming 25% of all transportation in the city to autonomous modes by 20308
Taking the impact to the next level
The UAE’s dedicated strategy towards AI and its initiatives to support the development of technologies places it in a strong position to develop itself as one of the leaders for AI in the region, and quite possibly the world. The government has demonstrated its commitment towards AI development in the country. However, as well as investment in AI, which it is clearly able to generate, the government will also need to create an environment which will allow the outcomes of these investments to become embedded in society. This will include, for example, preparing society and labour markets for the disruption through investing in education and skills development to allow people to adapt to the change. Similarly, legal institutions will also need to evolve to reflect the risks associated with AI technology.
Governments have a fundamental role in setting up an environment in which all stakeholders can effectively engage in the development and adoption of AI. Hence, the strategic focus on AI at the highest levels of government in the UAE, if properly harnessed, provides a strong foundation for AI-led growth.
The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia holds a clear vision for the future which points towards the development of AI-based technologies.
Saudi’s Vision 2030 and National Transformation Programme 2020 identify digital transformation as a key goal to activate economic sectors, to support industries and private sector entities, to advocate for the development of publicprivate business models and to ultimately reduce the country’s dependence on oil revenues through a diversification of the economy. Strategic objectives as part of this
vision include for example9:
- To improve the efficiency andeffectiveness of the healthcare sector through the use of information technology and digital transformation. To achieve this, it has set itself a target to increase the percentage of Saudi citizens who have a unified digital health record from 0 to 70% by 2020.
- To provide citizens with knowledge and skills to meet the future needs of the labour market. To achieve this, it has set itself a target to increase the percentage of internet users in Saudi from 63.7% to 85% by 2020.
Taking the impact to the next level
While there is some investment in AI in Saudi Arabia, supported by a commitment by the government to digitally transform the country, investment is currently largely driven through domestic sources, and in particular the country’s Sovereign Wealth Fund. In order to maintain momentum in the pace of technological advancement in the country, there is a need for it to attract more foreign investment which is currently constrained by the challenges in the business environment; in 2017, the country ranked 92 out of 190 countries in the World Bank’s Ease of Doing Business index. Addressing concerns raised by the business community will allow it to attract external investment which will bring with it skills and expertise to upskill the local population. This will also allow it to reduce the considerable youth unemployment placing a burden on the economy, which has increased from 24.1% to 32.6% between 1991 and 201710, by generating high-skilled employment opportunities.
AI at the industry level
The potential for AI adoption varies by industry. Research conducted by the International Data Corporation (IDC)11 finds that the biggest opportunity for AI in the Middle East and Africa region is in the financial sector where it is estimated that 25% of all AI investment in the region predicted for 2021, or $28.3 million, will be spent on developing AI solutions. This is followed by the public services, including education and healthcare, and the manufacturing sector.
The potential gains at the industry level is likely to depend on two broad factors:
- The ability to automate processes: labour-intensive sectors, such as retail and health, with greater scope for automation, are likely to see the largest initial gains from AI. These industries are expected to see significant labour productivity benefits from AI adoption.
- Sector-level use cases for product enhancement: sectors with compelling use cases in AI applications are more likely to innovate in early stages of AI development. PwC’s Data Analytics team in the US have developed an AI Impact Index12 through conducting a qualitative assessment to estimate the scale of product enhancements we will expect to see by 2030. The analysis assessed almost 300 use cases to identify the scope for product enhancements through personalisation, product quality, and time savings for consumers as well as scope for increased variety in products. The index indicates the highest potential for product enhancements in the health, automotive and financial services sectors.
The development of non-oil sectors through investment in AI technologies could strategically position the region for the years to come.
Despite the greater potential for direct gains in specific sectors, the gains are unlikely to remain concentrated in these sectors which develop and adopt AI technologies. As these sectors experience growth through the direct effects of AI, their demand for inputs from other sectors of the economy will also grow. Similarly, the increased wages associated with higher labour productivity in these sectors will also increase consumer demand in all sectors of the economy. These indirect and induced impacts of AI are likely to be felt by firms and consumers throughout the economy and will add to the total economic impact of AI.
Contribution of AI to industry in 2030
| Absolute contribution in 2030 (US$ billions) | Contribution of AI to Middle East GDP by industry | |
|---|---|---|
| Construction and Manufacturing | $99 | 12.4% |
| Energy, Utilities & Resources | $78 | 6.3% |
| Public sector, including health and education | $59 | 18.6% |
| Financial, Professional, Administrative Services |
$38 | 13.6% |
| Retail, Wholesale Trade, Consumer Goods, Accomodation and Food Services |
$23 | 19% |
| Transport and Logistics | $12 | 15.2% |
| Technology, Media, Telecommunications | $10 | 14% |
Helping you make the most of AI
PwC is working with governments and corporates across each of the different sectors highlighted in this report, to help them plan for and take advantage of AI to support their impact on strategy and performance.
If you would be interested in a consultation about the potential within your business, please feel free to get in touch.
- Overview of the approach
- What is AI?
Overview of the approach
Overview of the approach
Our approach seeks to quantify the total economic impact of artificial intelligence on the economies of 7 countries in the Middle East (Egypt, UAE, Saudi Arabia, and four countries have been grouped: Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman and Qatar) via productivity gains and consumption side impacts between now and 2030.
We have completed a number of stages of analysis in order to estimate the “first-round” impacts on jobs, productivity and product enhancements that have been inputted into our dynamic economic model in order to estimate the future size of the AI prize.
- On the production side, we focus on AI’s impact on labour productivity through automation. This required estimating the marginal impact of AI on productivity, the scale of automation expected to take place, the amount of AI replacing human labour and the amount of AI augmenting human labour for every industry in the Middle East between now and 2030.
- On the consumption side, we focus on AI’s impact on product enhancements which include increased quality, personalisation (i.e. product variety), as well as increased time-available for leisure or work.
We have used a dynamic economic model to evaluate the “net” impact of each channel on GDP and the economies as a whole.
Our results estimate the upwards pressure on GDP as a result of AI only, under the ceteris paribus assumption. Our results may not be directly reflected in future economic growth figures, as there will be many positive or negative forces that either amplify or cancel out the potential effects of AI (e.g. shifts in global trade policy, financial booms and busts, major commodity price changes, geopolitical shocks etc.).
What is AI?
In our broad definition, AI is a collective term for computer systems that can sense their environment, think, learn, and take action in response to what they’re sensing and their objectives.
Forms of AI in use today include digital assistants, chatbots and machine learning amongst others. In the table, we discuss the types of AI which include:
Assisted intelligence: Helping people to perform tasks faster and better.
Automated intelligence: Automation of manual/cognitive and routine/non-routine
tasks.
Augmented intelligence: Helping people to make better decisions.
Autonomous intelligence: Automating decision making processes without human
intervention.
As humans and machines collaborate more closely, and AI innovations come out of the research lab and into the mainstream, the transformational possibilities are infinite.
[1][12] PwC (2017), ‘Sizing the Prize: What’s the real value of AI for your business and how can you captialise?’
[2] For the purpose of this analysis, Middle East refers to the GCC plus Egypt
[3] WIPO, Cornell, INSEAD (2017), ‹The Global Innovation Index 2017 - Innovation feeding the world›
[4][11] IDC (2017), ‘Spending on Cognitive & Artificial Intelligence Systems to Undergo Sustained Period of Growth in the Middle East & Africa, says IDC’ [Press release]
[5] Smart Dubai 2021
[6] Khaleej Times (27 March 2017) ‘Smart lab accelerates AI move’’
[7][8] UAE Government (2017), UAE future 2030-2021
[9] Vison 2030 Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, ‘National Transformation Programme 2020’
[10] World Bank (2017), ‘Unemployment, youth total (% of total labor force ages 24-15)’
Contact us


Richard Boxshall
Global Economics Leader and Middle East Chief Economist, PwC Middle East
Tel: +971 4 304 3100








