National Budget 2025 - 2026
Taxation
Key Tax Measures
Tax, tax.. and tax! This year’s Budget delivers a clear message: the tax burden is rising - especially for banks, high-income earners, and corporates with annual chargeable income exceeding Rs24m. While the reduction in the limitation period for raising assessments is a welcome step toward efficiency and certainty, the introduction of the QDMTT raises serious concerns. As global tax rules tighten, we risk losing the competitive edge that has long attracted international business to our shores.
Corporate Tax
- Qualified Domestic Minimum Top-Up Tax (QDMTT)
- Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT)
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
- 80% tax exemption
- Investment Tax Credit (ITC)
- Exempt bodies
- Income tax holidays to Small & Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
- Restrictions of double/triple deductions effective from 01 July 2025
- Financial support schemes
- Financial support schemes (cont'd)
- Renewal and phasing out of schemes and allowances (Cont’d)
Qualified Domestic Minimum Top-Up Tax (QDMTT)
- Imposition of a QDMTT on resident subsidiaries and holding companies of MNEs resident in Mauritius on income derived as from 1 July 2025.
Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT)
Introduction of AMT on companies operating in the following specified sectors:
Hotels;
Insurance companies;
Companies engaged in financial intermediation;
Telecommunication companies.
Where the total tax payable by a specified company under the Income Tax Act (ITA) after allowable deductions but prior to foreign tax credits is less than 10% of its book profits, the specified company will be required to pay 10% of its book profits instead of its normal tax payable.
Book profit for the purposes of the AMT will be post adjustments for capital gains/ losses and dividends from resident companies.
The AMT will not apply to holders of a Global Business Licence (GBL) and companies benefiting from income tax exemptions and tax holidays.
No tax credits can be used to offset the AMT.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
- 50% of CSR Fund entitled to be spent by companies, instead of 25% currently.
80% tax exemption
80% tax exemption now available to licensed Virtual Asset Service Providers on income derived from the exchange, transfer, safekeeping and administration of virtual assets, subject to satisfying prescribed substance conditions.
80% tax exemption not available to banks on foreign source dividend.
Investment Tax Credit (ITC)
An ITC of 5% over 3 years (i.e. 15% in total) will be granted to qualifying small businesses or service providers with an annual turnover not exceeding Rs10m on the acquisition cost of new equipment (excluding motor vehicles) not exceeding Rs500,000 during the period from 01 July 2025 to 30 June 2030.
Unrelieved ITC may be carried forward for 5 years.
Exempt bodies
Corporate tax exemption granted to the National Guarantee Corporation Ltd.
Corporate tax exemption granted to companies implementing projects whereby at least 50% of the project is financed through grants or concessionary financing from a foreign state or a donor institution.
Income tax holidays to Small & Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
4-year income tax holiday to SMEs on conversion from sole trader or partnership to company no longer allowed where the SME is:
providing professional services;
a tourism operator; or
a training institution.
Restrictions of double/triple deductions effective from 01 July 2025
The following double deductions will be restricted to SMEs:
emoluments & training costs paid to employees in Rodrigues;
expenditure on the cost of setting up a crèche or Child Day Care Centre;
expenditure on acquisition of patents and franchises;
expenditure on acquisition of specialised software and systems;
expenditure on financing, sponsorship, marketing or distribution costs of a film.
150% deduction of expenditure on filing fees in respect of an application to a recognised arbitration institution in Mauritius restricted to SMEs.
Triple deduction of donation of a maximum of Rs1m to a charitable institution or NGO restricted to SMEs.
Financial support schemes
Introduction of a monthly Salary Compensation 2025 payable during the period from January to June 2025 as follows:

Financial support schemes (cont'd)
Introduction of the National Minimum Wage and Salary Compensation 2024 to export-oriented enterprises, irrespective of profitability, as follows:

Renewal and phasing out of schemes and allowances (Cont’d)
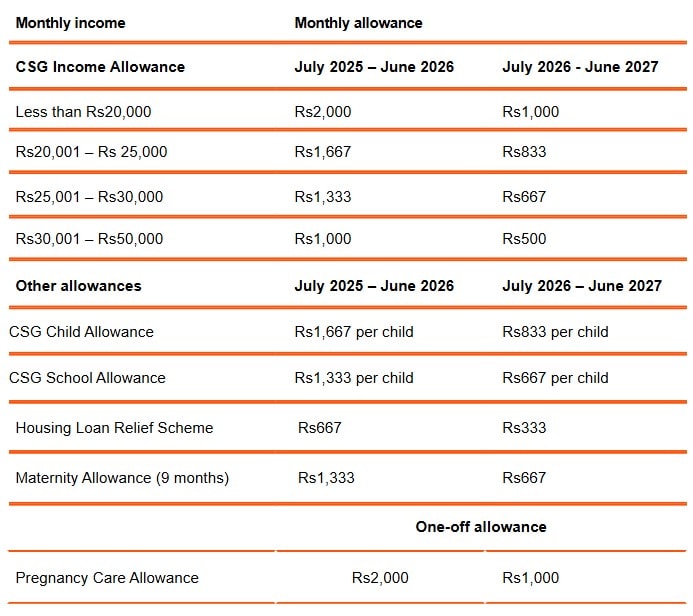
Renewal of the following allowances and phasing out over the next two years to 30 June 2027:
CSG Income Allowance;
CSG Child Allowance;
CSG School Allowance;
Pregnancy Care Allowance; and
Maternity Allowance.
Abolition of Independence Allowance effective 01 July 2025.
Household members who are beneficiaries under the Social Register of Mauritius (SRM) will continue to benefit from the above allowances. The monthly allowances payable will be as follows:
Personal Tax
- Revision of personal income tax rates and bands
- Tax exemption for persons aged between 18 and 28 years
- Fair-Share Contribution on high-income earners
- Taxation of car benefit
- Review of Personal Reliefs and Deductions
Revision of personal income tax rates and bands

Tax exemption for persons aged between 18 and 28 years
- An employee or a self-employed individual earning up to Rs1m annually will be exempt from income tax .
Fair-Share Contribution on high-income earners
- An individual earning annual net income exceeding Rs12m, inclusive of dividend income, will be required to pay a Fair-Share Contribution at the rate of 15% of his chargeable income after adding thereto any dividend income received during the year from domestic companies.
- For individuals earning above Rs24m, the tax rate will be 20%.
- The contribution will be collected under the PAYE system on income received by an individual and it will be applicable for 3 consecutive income years.
Taxation of car benefit
- The monetary values for car benefit are being reviewed as follows:

Review of Personal Reliefs and Deductions
The following personal reliefs and deductions will be removed:
- deduction of wage paid to a household employee;
- donation to charitable institutions;
- relief for adoption of animals; and
- angel investor allowance.
Value Added Tax
- Compulsory VAT registration
- Removal of Special Levy cap on banks
- Extension of zero-rated items
- VAT on specified digital services
- VAT refunds schemes
- Exempt bodies
- Companies
- Banks
Compulsory VAT registration
The VAT registration threshold decreased from Rs6m to Rs3m with effect from 01 October 2025.
Removal of Special Levy cap on banks
- Cap of 1.5 times of levy paid by a bank in the year of assessment 2017-2018 will be removed.
Extension of zero-rated items
Zero-rate VAT extended to:
fruit and vegetable purées for infants;
canned vegetables such as tomatoes and mushroom;
frozen packed vegetables such as potatoes, beans, spinach and mixed vegetables;
hairdressing services; and
CCTV systems
VAT on specified digital services
- Specified digital or electronic services provided by foreign suppliers will be subject to VAT with effect from 01 January 2026.
VAT refunds schemes
VAT refund on harvesting services will be granted to planters under the VAT Refund Scheme for Small Planters.
The VAT Refund Scheme on the construction of a residential building or the purchase of a residential apartment or house from a property developer will end on 30 June 2025.
Exempt bodies
- Where a project is financed to the extent of at least 50% from grants or concessionary financing, as approved by the Ministry of Finance, from a foreign State or a donor institution, the company implementing the project will be considered as an exempt body.
Companies
Corporates having annual chargeable income above Rs24m will be required to pay a Fair-Share Contribution at the rate of:
5% of chargeable income if they are subject to the standard tax rate of 15%;
5% of chargeable income for banks including on income derived by banks from transactions with non-residents and Global Business Companies; and
2% of chargeable income if they are subject to the reduced tax rate of 3%.
Banks
Banks will be required to make an additional contribution of 2.5% of their chargeable income from domestic operations (excluding income derived from transactions with non-residents and Global Business Companies).
- The contribution will not be applicable to:
companies holding a Global Business Licence;
companies exempt from payment of income tax or which have been granted tax holidays; and
income exempted from income tax.
- Corporates and Banks will not be allowed to offset any unused tax credits such as the foreign tax credit against the contribution payable.
- The contributions will be payable on a quarterly basis.
Smart City Scheme
- Removal of fiscal incentives
- Existing Projects
Removal of fiscal incentives
- Projects issued a Smart City Certificate or developer registration after 05 June 2025 will no longer benefit from key tax exemptions, including:
i.VAT exemption on buildings and infrastructure
ii.8-year income tax holiday on real estate income
iii.Customs duty exemption on import of machinery and materials for construction
iv.Registration duty and land transfer tax exemption on land transferred to Smart City Companies
v.Morcellement fee and land conversion tax exemptions
- Two exceptions apply:
i.Construction of a public transport station or terminal
ii.Projects under the National Regeneration Programme
Existing Projects
- Projects with development started before 05 June 2025 will no longer be eligible for:
i.Exemption from land conversion
ii.Exemption from customs duty on furniture, machinery and construction materials
- However, such projects will continue to benefit, for components with a valid Building and Land Use permit and construction started before 05 June 2025, from:
i.recovery of VAT paid on buildings, capital goods and construction of public roads
ii.income tax holiday on income derived from real estate activities
- A Smart City project, although outside the Morcellement Act, will be required to pay a fee equivalent to the Morcellement fee.
Other Taxes
- Property Tax and Housing Incentives
- Acquisition and Resale of Residential Property by Non-Citizens
- Acquisition and Resale of Residential Property by Non-Citizens (cont'd)
- Land Transfer Tax for Developers
- Motor Vehicle Excise Duty
- End of the Negative Excise Duty Scheme
- Registration Duty on vehicles
- Motor Vehicle Licence Fees
- Tourist Fee
- Sugar Content Excise Duty
Property Tax and Housing Incentives
Renewal of Housing Loan Relief Scheme and phasing out over the next two years to 30 June 2027.
The following schemes under the Registration Duty Act will be discontinued after 30 June 2025:
Home Ownership Scheme
Home Loan Payment Scheme
Acquisition and Resale of Residential Property by Non-Citizens
Registration duty on the acquisition of residential property by non-citizens under EDB schemes will increase from 5% to 10% of property value. The change applies to:
Smart City Scheme
Property Development Scheme (PDS)
Integrated Resort Scheme (IRS)
Real Estate Scheme (RES)
Invest Hotel Scheme (IHS)
Apartments in buildings with at least two floors above ground
Non-citizens selling residential property acquired under the above schemes (or qualifying apartments) will be subject to land transfer tax at the higher of:
10% of the property value, or
30% of the gain realised on the resale.
Acquisition and Resale of Residential Property by Non-Citizens (cont'd)
Where a non-citizen acquires such a property on resale, they will also be liable to the 10% registration duty.
The new rate will apply on deeds registered after publication of the Finance (Miscellaneous Provisions) Act 2025, regardless of prior reservation agreements.
Land Transfer Tax for Developers
Promoters selling residential units under the above schemes, including qualifying apartments, will now be subject to land transfer tax at 10%, instead of 5%, at time of registration.
Motor Vehicle Excise Duty
New rates of excise/customs duty on vehicles will apply from 6 June 2025 based on engine size and vehicle type (conventional, non-plug-in-hybrid, plug-in hybrid)
Electric cars up to 180KW will attract a duty of 15% and 25% for those above 180kW
A transitional provision will allow previously applicable rates to continue for vehicles already shipped or held in bonded warehouses as at 05 June 2025, provided clearance is completed by 30 June 2025

End of the Negative Excise Duty Scheme
- The Negative Excise Duty Scheme for electric vehicles will officially end on 30 June 2025 and will not be renewed.
Registration Duty on vehicles
From 01 July 2025, Registration Duty will be abolished on the sale and transfer of domestic pre-owned vehicles.
For first registrations, duty will be increased by 30%.
Motor Vehicle Licence Fees
The 50% concessional rate previously applied to hybrid and electric vehicles will be abolished and these vehicles will now attract the full amount corresponding to the class of conventional vehicles.
The 3-month and 6-month payment options for licence fees remain available.
Tourist Fee
A Tourist Fee of €3 per night per tourist will be applicable from 01 October 2025 for stays in
Hotels
Guesthouses
Tourist residences
Domaines
Tourists under 12 years will be exempted from payment of the fee.
The fee will be collected by designated establishments and remitted monthly to the MRA.
Sugar Content Excise Duty
From 06 June 2025, the excise duty on sugar content in sweetened products will increase from 6 cents to 12 cents per gramme of sugar.
Additionally, from 01 October 2025, these 12 cents per gramme will also apply to:
Chocolates
Ice cream
Tax Administration
- Power to raise assessments
- Capping on penalty and interest
- Tax Dispute Settlement Scheme (TDSS)
- Voluntary Disclosure Settlement Scheme (VDSS)
- Tax Arrears Settlement Scheme (TASS)
- Registration of tax agents
- Payment of tax in foreign currency
- Tax Administration: Income Tax
- Tax Administration: Customs Act
- Value Added Tax Act
- Excise Act
Power to raise assessments
Subheading title text tab 1
- The Mauritius Revenue Authority's power to issue assessments for past years will be limited to a two-year period, except in exceptional circumstances.
Capping on penalty and interest
Penalties and interest will be capped to 100% of the tax amount due.
Further, penalties and interest for unpaid taxes will be reduced by 50%, provided they do not pertain to withholding taxes collected on behalf of the Government.
Tax Dispute Settlement Scheme (TDSS)
A one-off TDSS will be introduced to reduce the backlog of tax cases under dispute or litigation at the Assessment Review Committee (ARC), the Supreme Court (SC) or Privy Council (PC).
Under TDSS, taxpayers who withdraw their cases from the ARC, the SC, or the PC and have outstanding tax claims will be granted a full waiver of penalties and interest.
- The Scheme applies to cases under litigation as of 05 June 2025 and runs until 31 March 2026. Taxpayers must pay the tax due by 31 March 2026 to benefit from the Scheme.
- No tax, penalty, or interest paid will be refundable under this Scheme, except where the case is before the SC and the tax has already been settled.
Voluntary Disclosure Settlement Scheme (VDSS)
A second one-off scheme, the VDSS, will be introduced to encourage taxpayers who have undeclared or under-declared income or taxable supplies to come forward and regularise their tax affairs.
Under VDSS, a taxpayer will benefit from a full waiver of penalties and interests.
The VDSS will be available until 31 March 2026, with all payments required by that date.
For income tax purposes, the VDSS will cover undeclared or under-declared income for the Year of Assessment 2024/25 and earlier, excluding returns due in June 2025.
For VAT purposes, the VDSS will apply to undeclared or under-declared taxable supplies for periods ending on or before 30 April 2025.
No tax, penalty, or interest paid will be refundable under this Scheme under any circumstances.
Tax Arrears Settlement Scheme (TASS)
- Extension of TASS providing full waiver of penalties and interests for tax debt and tax arrears outstanding as at 30 June 2025, provided the taxpayer registers by 30 November 2025 and pays the tax in full by 31 March 2026.
Registration of tax agents
All tax agents will henceforth be required to register with the MRA.
Members of the Mauritius Institute of Professional Accountants and law practitioners will be deemed registered under the law.
Payment of tax in foreign currency
- Businesses earning at least 50% of their annual turnover in foreign currency will be required to settle their tax liabilities in foreign currency.
Tax Administration: Income Tax
Arm’s length test
The scope and methodology of the application of the arm’s length principle will be reviewed.
Tax ruling
The fees payable for a Income Tax ruling will be increased to:
(A) Rs3,000 for an individual; and (B) Rs50,000 for any other person.
Tax Administration: Customs Act
Deferred payment in respect of VAT on capital goods
- Under the deferred VAT scheme, a VAT-registered person is not required to pay VAT on the import of capital goods of a value of Rs1m or more. However, the VAT-registered person should declare the non-payment in his VAT return. To further ease the cash flow of businesses, the threshold for the import value of capital goods will be reduced to Rs500,000 or more.
Extension of Objection and Appeal Payment Requirements to Customs Legislation and Excise Act
- The Income Tax Act and VAT Act make provision for any aggrieved person lodging an objection at the Objection Directorate of MRA or an appeal at the Assessment Review Committee (ARC) to make a payment of 10% and 5% respectively of the amount of taxes underpaid. Similar provision will be made in the Customs Act, Customs Tariff Act and Excise Act to discourage frivolous objections and appeals with a view to delaying the payment of taxes due.
Failure to provide detailed grounds of objection
- If a person disputes the tax amount assessed by the MRA but has not specified the detailed grounds of the objection, the MRA may treat the objection as lapsed. However, the individual will retain the right to appeal against the MRA’s decision
- This new provision will be included in the various customs laws in the following cases:
- payment of taxes under protest by the person;
- non-acceptance by MRA of a claim for refund of duty paid in excess made by the person;
- claim by MRA for an erroneous refund or reduction in taxes;
- claim for underpayment of taxes by MRA;
- claim for taxes due by MRA where a person sells goods on which exemption has been granted before the expiry of 4 years from the date of the exemption; and
- claim for excise duty unpaid following a stocktaking of excisable goods in a factory.
Value Added Tax Act
- During the financial year 2025-26, suppliers making a turnover of more than Rs80m will join the e-invoicing system.
- Credit for input tax on rented parking is disallowed, except for motor vehicles used in the furtherance of a business.
- MRA will be empowered to use the best of its judgement when making an assessment of taxes due where it is not satisfied with the adequacy or correctness of records kept.
- An administrator, executor, receiver or liquidator appointed to manage or wind up a company will be liable to pay the VAT due in the order of priority of payments to preferential creditors set out by the Insolvency Act.
- Reverse charge on supply of services received from abroad will apply to all VAT registered persons, including banks receiving services from a foreign supplier.
- A person seeking a ruling has no right of representation against the ruling at the ARC.
- VAT will be applicable on supply made to a foreigner who is outside Mauritius at the time the service is performed, if the service is utilised in Mauritius.
- A holder of a Pleasure Craft Licence issued by the Tourism Authority will be required to compulsorily register for VAT purposes irrespective of his turnover.
- The fees payable for a VAT ruling will be increased to:
- (A) Rs3,000 for an individual; and (B) Rs15,000 for any other person.
- A person will be liable, on conviction, to a fine not exceeding Rs100,000 and to imprisonment not exceeding 3 years upon failure to submit information requested by MRA.
- Failure by a person to give access to computers and other electronic devices requested by MRA will be an offence and the person will, on conviction, be subject to a fine not exceeding Rs200,000 and to imprisonment not exceeding 5 years.
- A fine not exceeding Rs500,000 will be applicable for offences relating to:
- making an incorrect return or statement ;
- making an incorrect claim for repayment in respect of capital goods;
- giving incorrect information in respect of tax liability;
- a person claiming to be VAT registered when he is not; or
- obstructing an officer of MRA in his functions.
- The fine will henceforth be an amount not exceeding Rs1m for:
- failure to register for VAT purposes;
- failure to submit a VAT return and pay any tax due; or
- submission of false returns, books, records, VAT invoices, documents or information with intent to evade VAT.
- The fine for the following offences has been increased to Rs100,000:
- failure to keep records, produce books and records or provide any other information required by MRA for the purpose of ascertaining the tax liability of a person;
- failure of a VAT registered person to issue a VAT invoice;
- failure of a VAT registered person to change his taxable period from quarterly to monthly when his annual turnover exceeds Rs 10 million; and
- contravening any other provisions of the VAT Act/Regulations other than (1) a person claiming to be VAT registered or (2) obstructing an officer of MRA in his functions.
Excise Act
A penalty not exceeding 50% and interest at the rate of 0.5% per month will be imposed on excise duty considered unpaid following a stocktaking of excisable goods in a factory.
When Customs issues a tax claim to a manufacturer following a stocktaking of excisable goods, the manufacturer may only appeal through the MRA’s Objection Directorate.
The MRA will have the option to give public notice of the list of excise licences issued, renewed, transferred, cancelled or surrendered at the end of every year through publication in the Government Gazette, a newspaper or in electronic form.