{{item.title}}
{{item.text}}

{{item.title}}
{{item.text}}
The Global Hopes and Fears survey has drawn responses from nearly 54,000 individuals in 46 countries and territories, including 1,563 Middle Eastern respondents from KSA, UAE, Egypt and Qatar.
It examines the attitudes, mindsets and challenges faced by a workforce enthusiastic about embracing digitisation and reducing carbon emissions in the wider region. This workforce is in sync with the region’s collective vision of a sustainable future and the need for economic diversification.
The survey also offers an exciting perspective into Gen Z, who are demanding a more supportive work environment.
The Middle East survey results reveal three key themes: Individuals must enhance and refine their skills to thrive in their jobs in the next five years; excitement surrounding artificial intelligence and a strong yearning for increased autonomy and job satisfaction.
These findings shed light on the pressing issues that demand attention and action from organisations to empower the workforce and propel the region toward a prosperous future. Business leaders engaging with this workforce must understand their hopes and fears and empower them with the right tools to innovate and transform.
In a region that is undergoing transformative changes on multiple fronts, respondents recognise that upskilling is essential to unlocking the Future of Work.
52% of the individuals surveyed in the region, compared to the global 36%, believe their jobs will change significantly in the next 5 years, requiring them to acquire new skills and capabilities. 61% of respondents stated they possess a distinct understanding of how their skills are anticipated to evolve.
Interestingly, 54% of regional employees also expressed their trust in employers’ ability to stay updated with the latest trends and encourage them to apply their newly acquired skills.
This can be attributed to a mature, enabling regional ecosystem of future-ready Middle Eastern governments and business leaders that have embraced digitisation and decarbonisation to diversify their economies and position themselves for sustainable economic growth and development.
Leapfrogging past more mature governments in the digital space, regional leaders are deploying advanced technologies, such as cloud computing, AI and machine learning, in their operations. For instance, the UAE Roads and Transport Authority has reported that Chatbot Mahboub has contributed a 40% reduction in the RTA’s live chat call centre within 2 years. This trend has been reiterated in our recent PwC 26th CEO survey, where 84% of respondents in the region said they would invest in automation processes as they prepare to advance their digital transformation agendas in the next few years.
The twin transitions of digitisation and decarbonisation are reshaping how we live, operate and think about the future. Emerging technologies, environmental awareness, rapid urbanisation, the circular economy, greening and automation directly impact the labour market, creating new occupations that require new skill sets and making other employment opportunities and skills obsolete.
In the Middle East, as key economies drive forward with their green initiatives, employees have displayed a heightened awareness of the importance of green skills compared to their global counterparts. This indicates a strong recognition of the region’s emphasis on sustainability and the growing demand for environmentally conscious expertise.
Notably, among the regional respondents, 62%, approximately two-thirds more than the global figure, expressed the belief that green skills would play a crucial role in shaping their careers. Furthermore, a significant 57% expressed confidence in their employers’ commitment to equipping them with the necessary tools and opportunities to enhance their green skills. These statistics strongly align the workforce and the region’s green agenda, highlighting a shared vision for sustainable growth and professional development.
The importance of unlocking sustainability skills to support the region in achieving its climate ambitions and advancing towards a sustainable future is a key highlight of the PwC 2023 Middle East report, which examines the employers attitudes on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues. The report emphasises the shortage of internal expertise and skills necessary to successfully implement ESG initiatives, including specialised roles such as net-zero accounting specialists and risk managers. This skills gap is not limited to the Middle East but is a global challenge that must be addressed to effectively drive sustainable practices worldwide.
The significance of green skills was evident among the respondents, with 73% in Qatar, 61% in the UAE, 60% in Saudi Arabia and 59% in Egypt recognizing their importance.
Additionally, leadership skills emerged as a top priority in the region, with 83% of respondents considering them critical, compared to 63% globally.
As digitisation initiatives continue to flourish in the regional economy, 75% of Middle East respondents emphasised digital skills as one of the top priorities for their careers in the next 5 years, surpassing the global figure of 57%. 77% of individuals surveyed expressed the need for specialist technical skills, compared to 56% globally, while 76% recognised the value of analytical and data skills, in contrast to 58% globally.
In a world where companies actively strive to comprehend the capabilities of Generative AI and navigate its potential disruptions, survey respondents from the Middle East have displayed a positive attitude towards artificial intelligence. They have demonstrated trust in AI and an eagerness to embrace its integration in their workplace. They have recognised the positive impact of AI on their jobs, surpassing their global counterparts. Nearly half of the respondents view AI as valuable to their productivity.
Middle Eastern governments and businesses have wholeheartedly embraced AI and advanced technologies. Our 2018 report on the potential impact of AI in the region emphasises that AI holds the potential to foster the development of innovative businesses and entirely new business models. At that time, the estimated impact of AI on the Middle East economy was a staggering US$320 billion, underscoring its transformative potential for the region. Given the recent rapid developments in AI, we expect this estimated figure to be much greater now.
However, it is worth noting that millennials showed a lower level of confidence in their capacity to learn new skills offered by AI at 31%, while Gen X respondents demonstrated a similar sentiment at 29%. In contrast to them, Gen Z displayed relatively greater optimism with only 19% expressing less confidence.
Just when we thought the era of the Great Resignation was behind us, employees in the region are now more inclined than ever to seek new employment opportunities.
According to our survey findings, a significant 39% of respondents in the Middle East expressed a higher likelihood of switching employers in 2023, compared to 30% reported last year. Notably, this trend is predominantly driven by younger employees, with 37% of Gen Z and 40% of millennials leading the movement.
On a global scale, the desire to change jobs within the next 12 months has also increased, with 26% of respondents indicating their likelihood of seeking new employment opportunities, up from 19% in 2022.
The survey results indicate that managers, in particular, demonstrated a significantly higher inclination to change employers. Several recurring factors emerged as driving forces when exploring the motivations behind employees wanting to switch jobs. These included the pursuit of higher salaries, the aspiration for job fulfilment, and the desire for increased autonomy in the workplace. These compelling reasons shed light on the dynamics shaping employees’ career choices in the current landscape.
Building upon last year’s prominent theme of flexibility, this year, employees have further emphasised their desire for greater autonomy over their work approach. A notable statement echoed by respondents is, "I can choose how I do my work in a way that suits me." This sentiment is shared by 55% of millennials, 54% of Gen X and 48% of Gen Z respondents, highlighting these generations’ distinct expectations regarding traditional work arrangements.
The COVID-19 pandemic played a significant role in shaping these changing perspectives, as stay-at-home measures led to the emergence of non-traditional work arrangements (NTWAs). These arrangements encompassed intermittent work patterns, remote work, and the option to work from one’s own office or home office. These NTWAs granted employees the freedom to determine their work schedules and dress codes, providing them with more flexibility than traditional employment norms.
As Gen Z enters the workforce, the labour market witnesses shifting expectations. This generation exhibits particular preferences for flexible working arrangements and feels less comfortable and aligned with their company culture than their more senior peers.
Last year, the Middle East Hopes and Fears survey provided valuable insights into the behaviour of Gen Z individuals (born between 1995-2010) in the workplace. This generation demonstrates unique concerns regarding the support and resources offered by employers for ethical decision-making. They also express lower confidence in employer transparency regarding diversity and inclusion efforts. Additionally, Gen Z individuals are more inclined to engage in frequent discussions with colleagues about social and contemporary issues and exhibit a stronger preference for full-time or predominantly remote working arrangements.
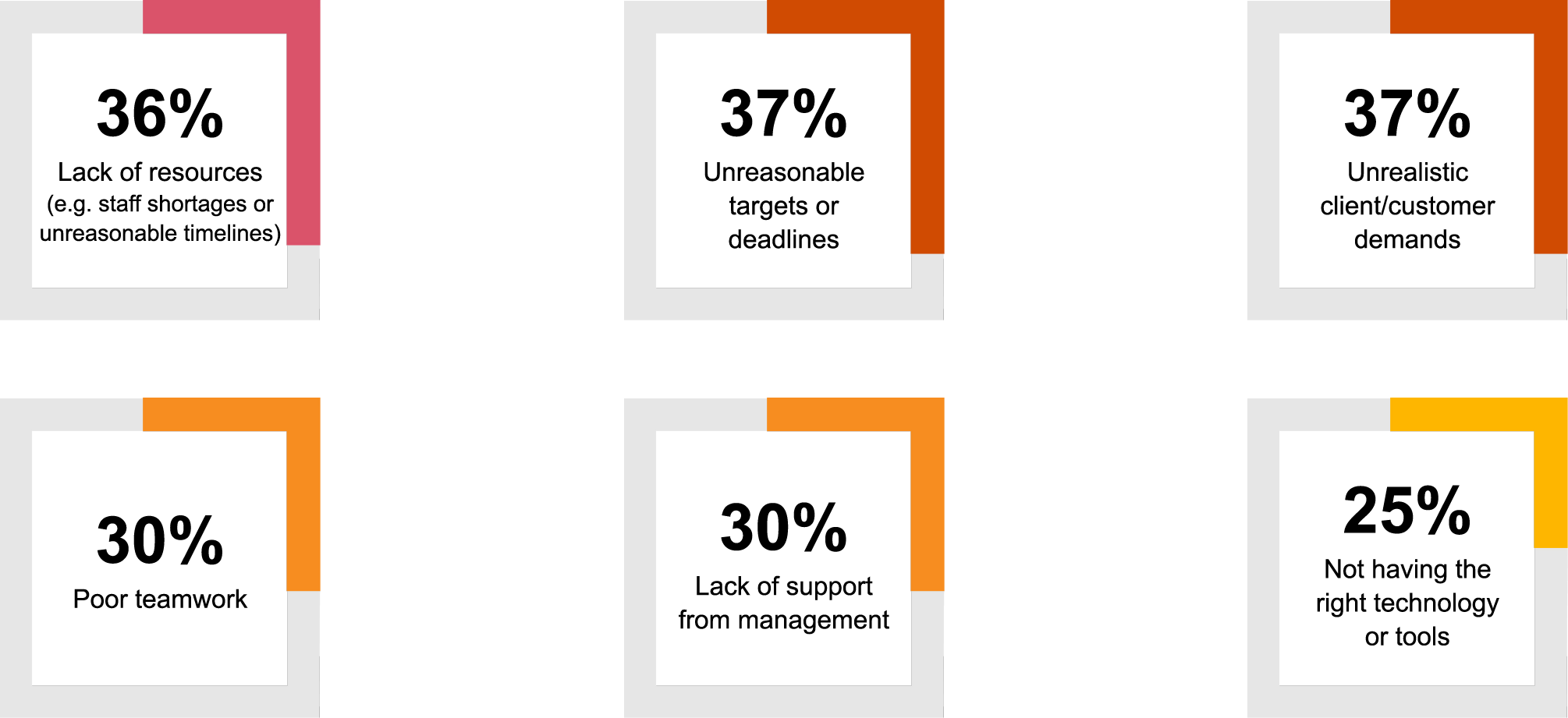
This year, the trend continues as Gen Z seeks a supportive work environment. Globally, over one-fifth of respondents reported frequently facing unmanageable workloads in the past 12 months, with half of them attributing this challenge to a lack of resources.
Read more about the challenges Gen Z faces in the workplace here.
Question: Which of the following factors have created unmanageable workloads for you in the past 12 months?
(Showing only ‘Gen Z’ responses)
The survey results highlight global workforce trends that underscore the imperative for business leaders to prioritise upskilling initiatives in order to cultivate a more aware workforce that understands what’s needed to perform their jobs in the next five years.
Upskilling must become integral to boardroom discussions as companies navigate the rapid transformations and diversification driven by digitisation and decarbonisation. The development of green skills and a comprehensive understanding of the responsible use of AI is pivotal for businesses to address. Additionally, fostering greater autonomy among employees should be a key agenda for business leaders.
It is essential for companies to recognise the emergence of a new generation, Gen Z, in the workforce. By understanding the unique characteristics of Gen Z, organisations can create an inclusive workplace environment where everyone feels supported, valued, and heard. This will attract and motivate top talent, embrace age diversity in organisations, strengthen engagement and boost productivity.
Middle East organisations must take specific actions:
Prioritise the roll-out of upskilling programs, nurturing a future-ready and resilient workforce through continuous learning and development
Integrate the twin transitions of technology and decarbonisation at the core of their strategies, enabling sustainable growth and resilience as economies strengthen their diversification efforts
Focus on agility and adaptability to stay ahead of the rapid pace of change and avoid falling behind in a dynamic business environment
Encourage leaders to actively engage with employees at all levels and embrace innovative and flexible work approaches to create a culture of trust
Create a compelling employee value proposition aligned with the evolving business landscape and changing expectations as newer generations enter the workforce